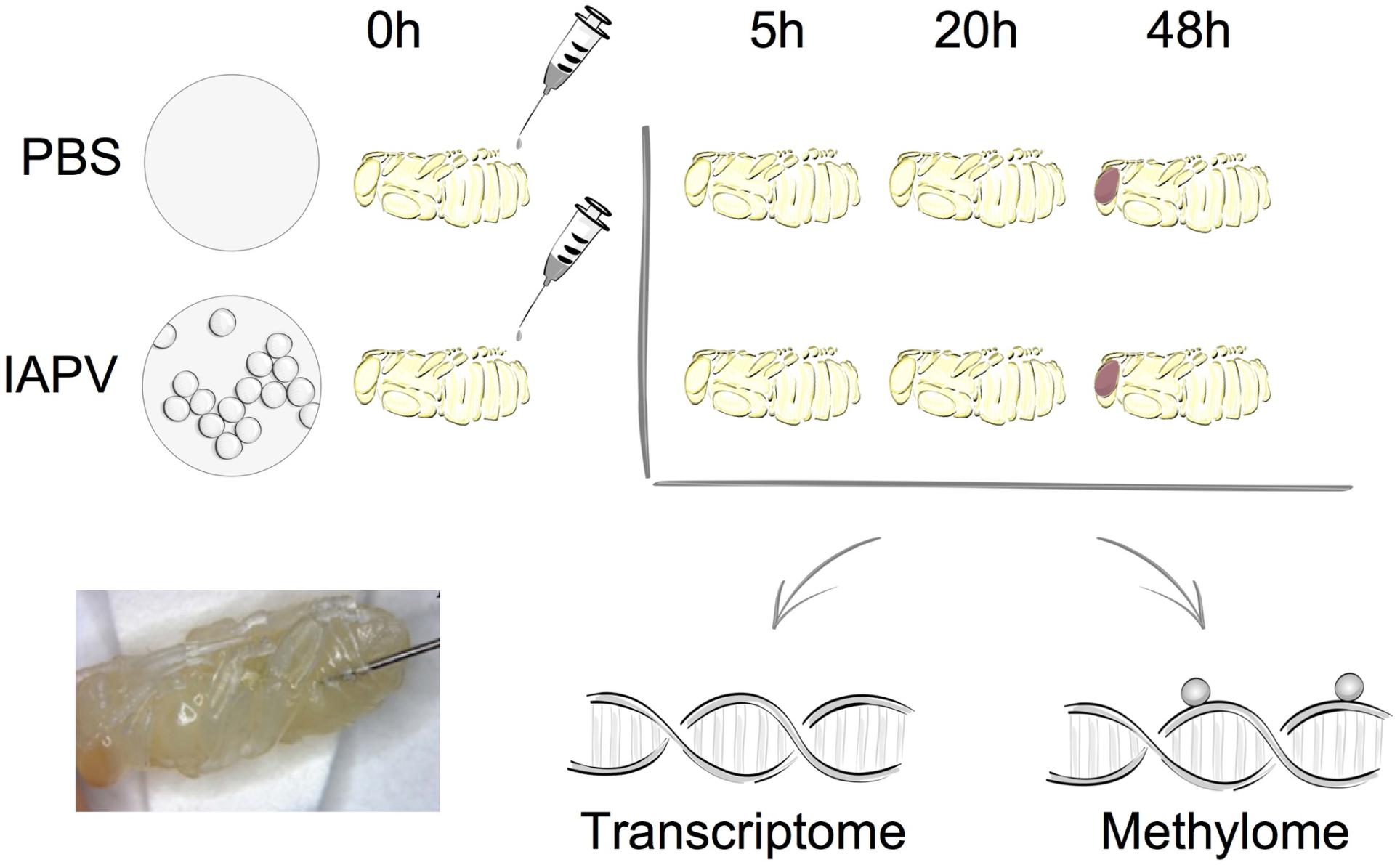
Figure 1. Overall experimental design. The two experimental groups included either sham treatment (PBS injection) or Israeli Acute Paralysis Virus (IAPV) inoculations via injection. At each investigated time point (5, 20, or 48 h post-injection) three biological replicates were collected, each consisting of one whole pupa that was individually processed for further transcriptomic and methylomic analyses. Li-Byarlay H, Boncristiani H, Howell G, Herman J, Clark L, Strand MK, Tarpy D, Rueppell O, 2020. Transcriptomic and epigenomic dynamics of honey bees in response to lethal viral infection. Frontiers in genetics. 11, 1056
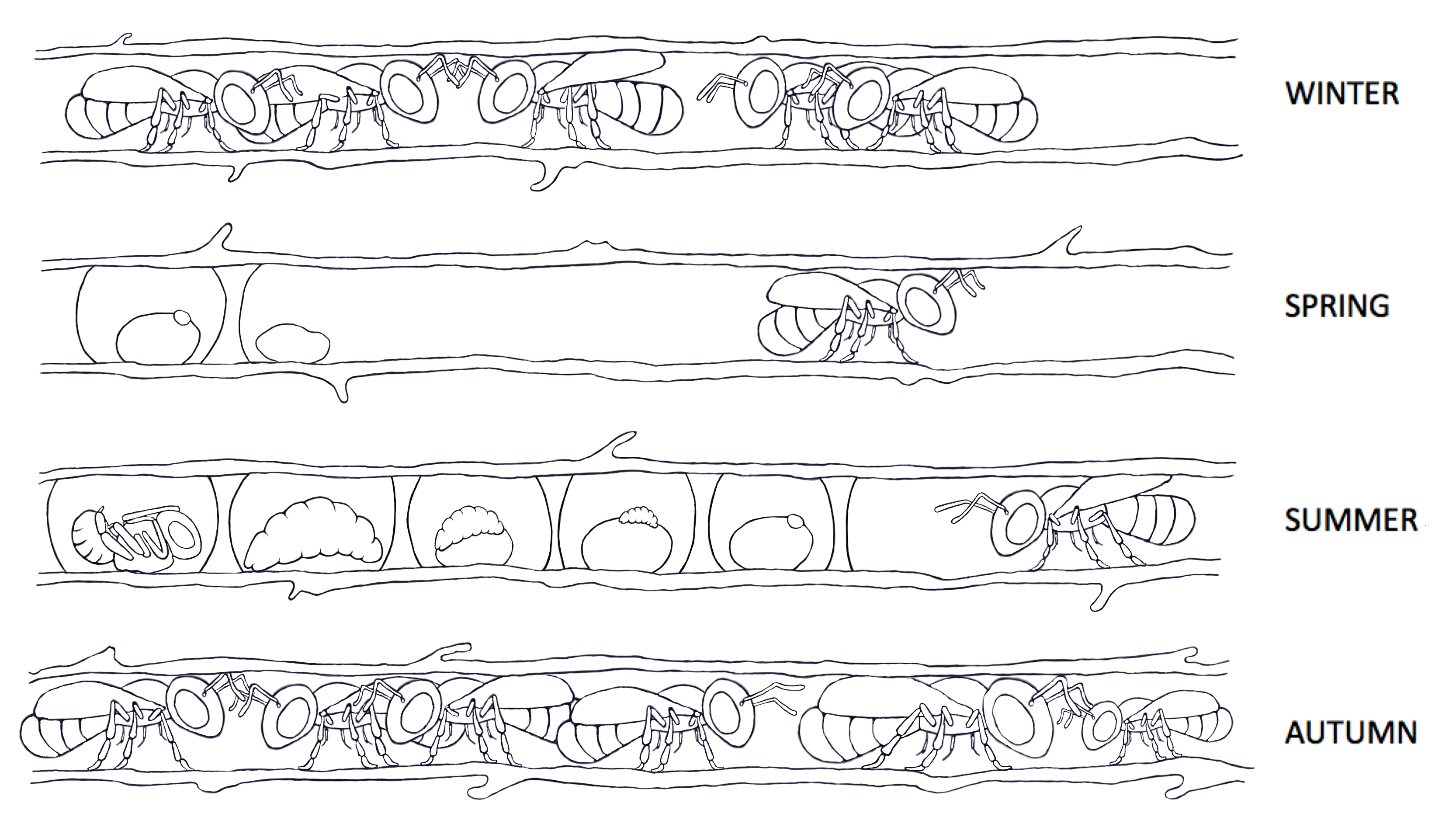
Colony cycle of Ceratina calcarata. Five time points assayed for comparative transcriptomic analyses: 1 – spring mothers, 2 – summer mothers, 3 – autumn mothers, 4 – autumn dwarf eldest daughters, and 5 – autumn regular daughters. Rehan SM, Berens AJ, Toth AL (2014). At the brink of eusociality: transcriptomic correlates of worker behaviour in a carpenter bee. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 14: 260
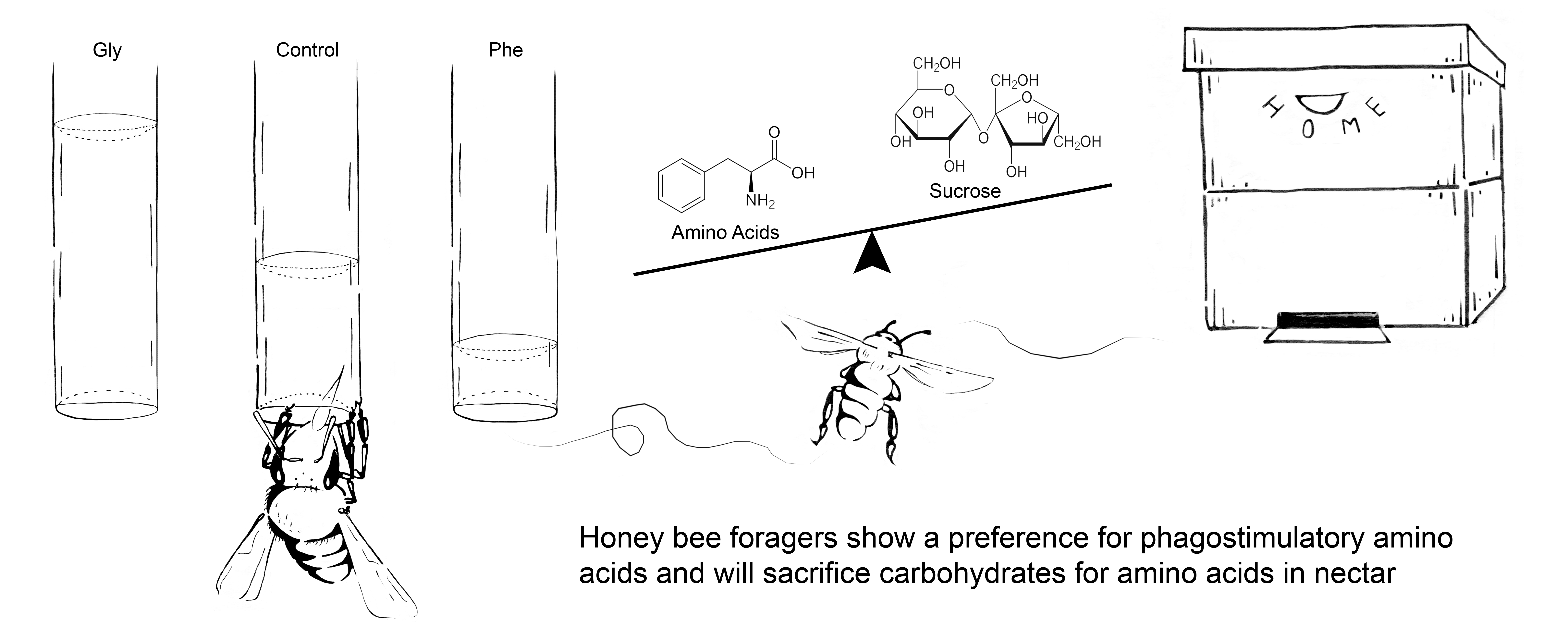
Hendriksma HP, Oxman KL, Shafir S (2014) Amino acid and carbohydrate tradeoffs by honey bee nectar foragers and their implications for plant-pollinator interactions. Journal of Insect Physiology. 69:56-64
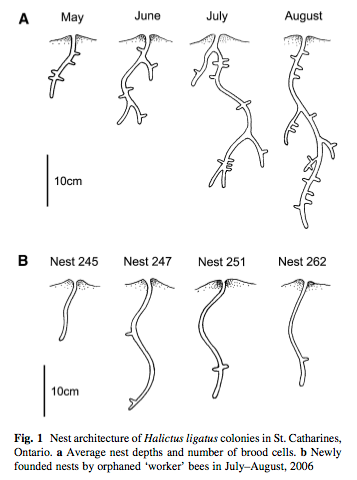
Rehan SM, Rotella A, Onuferko TM, Richards MH (2013) Colony disturbance and solitary nest initiation by workers in the obligately eusocial sweat bee Halictus ligatus. Insectes Socioux. 60(3): 389-392.